Botanical medicine, also known as herbal medicine, is the science and practice of using medicinal plants and extracts to improve overall health, support wellness, and treat acute and chronic disease.
We have practiced botanical medicine based on traditional Chinese medicine for over 35 years. There are a lot of successful cases in our clinic. Herbal supplements can be adapted to treat difficult infertility conditions such as POI, POF, PCOS, endometriosis and repeated pregnancy loss. It is very effective to combine with Chinese herbal medicine in the ÎVF support plan.
- Antral Follicles Counts ( AFC)
Antral follicles are the most primitive grade 3 follicles that develop in the ovaries and are important indicators of female ovarian function.
With the help of vaginal ultrasound or color Doppler ultrasound, doctors can count the number of antral follicles to evaluate a woman’s ovarian function and reproductive ability.
The number of antral follicles is closely related to the success rate of IVF. The greater the number of antral follicles increase the number of mature follicles obtained after ovulation promotion, increasing the likelihood that any available eggs would be accepted during egg retrieval process; the more embryos used for transfer, the better.
Antral follicles are critical to the success of IVF. The data from our clinic show that botanical medicine can significantly increase the number of antral follicles.
There were 43 patients with antral follicle count data before and after treatment. The patients were between 30 and 43 years old, and the median age was 39 years.
We compare the number of antral follicles before and after herbal treatment with the number of antral follicles after 3 months of taking the herbal medicine. The results in Figure show that AFC has a significant upward trend after treatment.
The results in the Figure 1 suggest the herbal supplements may increase the number of antral follicles by blocking the apoptotic pathway of eggs, thereby improving female reproductive capacity and helping to increase the success rate of IVF.

Figure 1: The AFC comparison before and after herbal treatment in 43 cases
- Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH)
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein. AMH is secreted by granulosa cells in the follicle. The more ovarian follicles, the higher the concentration of AMH in the serum.
The increase in AMH not only reflects the increased function of follicular granulosa cells, but also reflects the increase in the number of antral follicles.
Granulosa cells are not only a source of nutrients for oocyte development, but also a place to aromatize androgens to produce estrogen. The improvement of AMH suggests an improvement in egg quality and ovarian axis function.
Therefore, reproductive doctors often use it as one of the indicators of ovarian reserve, which can be used to predict female fertility and IVF success rate.
We collected clinical data of 14 patients and compared them before and after. The patients were between 32 and 41 years old, and the median age was 37.5 years.
The results in Figure 2 showed that AMH had a significant upward trend after treatment.
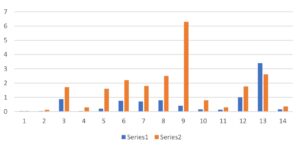
Figure 2: The AMH comparison before and after herbal treatment in 14 cases
- Third Day Embryo Counts
After egg retrieval and fertilization using IVF technology, the embryonic development is as follows:
Day 1: Sperm and egg are combined and fertilized, and two pronuclei appear;
Day 2: Embryo develops to 4 cells;
Day 3: Embryo develops to 8 cells;
Day 4: Embryo development to morula stage;
Day 5 and 6: Embryo development to blastocyst stage.
We collected the three-day embryo counts of 16 patients before and after treatment. The patients were between 30 and 43 years old, and the median age was 37 years.
The results showed that the number of three-day embryos obtained by the patients increased significantly after treatment with the herbal supplements.
The results in the Figure 3 suggest that the patients have noticed a significant improvement in egg quality after taking the herbal supplement —especially the enhancement of the mitochondrial function of the eggs, so as to provide enough energy to promote embryonic development.
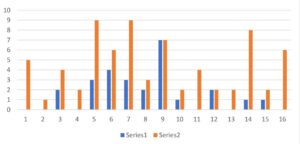
Figure 3: The Third Day Embryo Counts comparison before and after herbal treatment in 16 cases
- Blastocyst
Compared with the third-day embryo, the fifth-day blastocyst is a more well-developed embryo. Generally speaking, the implantation rate of embryos on the third day is 20-30%, and the implantation rate of embryos in the blastocyst stage on the fifth day is 40-50%. Therefore, the increase in the number of blastocysts is a critical factor in the success of IVF.
A total of 17 patients had blastocyst count data before and after treatment. After their comparison, the patients were between 33 and 46 years old, and the median age was 38 years.
The results showed in Figure 4 that blastocysts had a significant upward trend after herbal treatment. This result further suggests that the botanical medicine have the effect of blocking egg apoptosis and improving mitochondrial function.
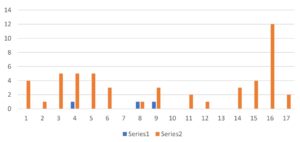
Figure 4: The Fifth Day Blastocyst Counts comparison before and after herbal treatment in 17 cases
- Euploid Blastocysts (uploid)
Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) refers to the analysis of 23 pairs of chromosomes of embryos through biopsy of embryonic cells during IVF treatment before the embryos are transferred into the uterus.
If the number of chromosomes of the blastocyst is normal, then This embryo is called an Uploid blastocyst.
With the increase of age, the quality of women’s eggs gradually decreases, and the aneuploidy rate of embryos increases.
Non-euploidy is the main cause of embryo implantation failure, spontaneous abortion, and congenital malformations.
It is also a key factor leading to IVF failure and the leading cause of early abortion in older women.
To further confirm the effect of botanical medicine on the improvement of egg quality, we collected the changes in the number of euploid blastocysts before and after herbal treatment in 14 patients.
The patients were between 32 and 42 years old, and the median age was 38.5 years. As shown in Figure 5, most patients cannot obtain euploid blastocysts (uploid) before treatment, which leads to complete failure of IVF.
However, after treatment, 11 patients obtained euploid blastocysts. One of the patients obtained 12 euploid blastocysts after treatment with the herbal supplement.
This result further suggests that in addition to inhibiting the apoptosis pathway and promoting mitochondrial function, the prescription may also protect the egg DNA from damage and prevent gene mutation.
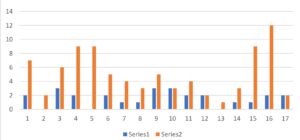
Figure 5: The Euploid Blastocysts (uploid) counts comparison before and after herbal treatment in 17 cases

Comments are closed